
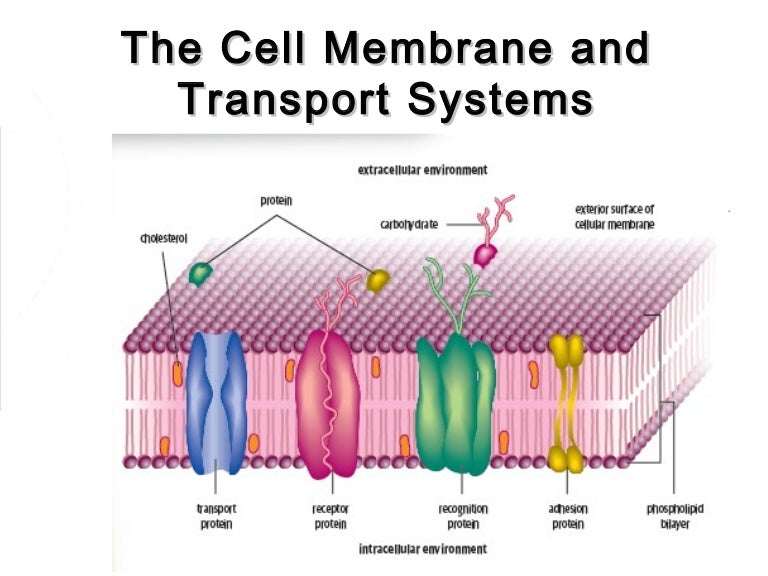
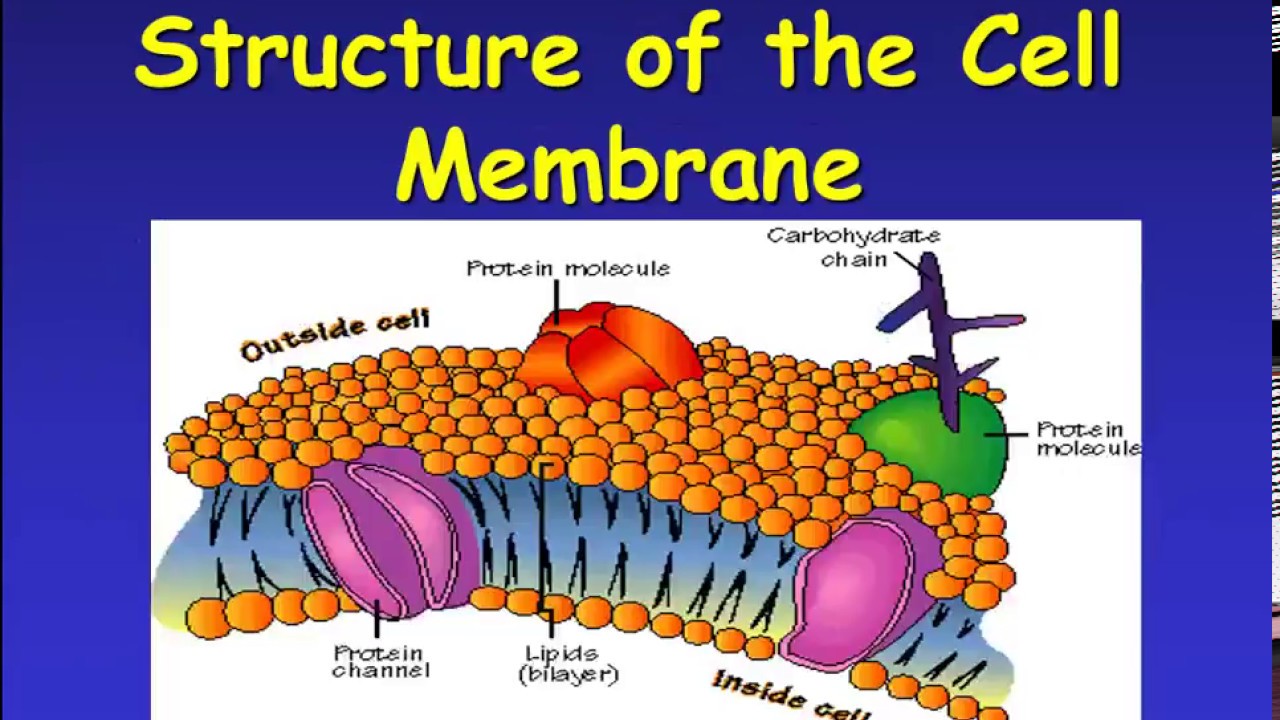
Cell membranes and Transportįluid Mosaic Model Phosopholipids, cholesterol and proteinsform a mosaic (pattern) within the cell membrane AS Biology. Phospholipids act as a barrier to most water soluble substances.HYDROPHILIC heads (phosphate group)- LOVE water!! AS Biology.HYDROPHOBIC tails (the fatty acid portion)- HATE water!!.Phosphate head is hydrophilic, fatty acid tail is hydrophobic.Lipid with a phosphate group in place of one fatty acid chain.Cell membranes and TransportĬell Membranes: Every cell is enclosed by a double layer of phospholipids. Cell communication recognition AS Biology.Selectively Permiable- regulates which particles (nutrients, wastes) can enter and exit the cell.How does its structure allow it to carry out its functions?.What are the functions of the cell membrane?.Outline the roles of the plasma membrane, and the roles of membranes within cells.Outline the roles of phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins and glycoproteins in membranes.

Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and explain the reasons for its structure.What is the structure of the membranes of our cells?ĭiffusion Osmosis Selectively Permeable Passive Transport Active Transport Key words to know!.How does a bubble model the fluid nature of a cell membrane?.Does it look like the surface of the bubble moves? How can you tell?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
